Best Practices for Email Deliverability
As part of your Content Catalyst subscription you will have access to a Sendgrid subaccount using the Sendgrid "Teammates" feature
Sendgrid Teammates
As part of your Content Catalyst subscription you will have access to a Sendgrid subaccount using the Sendgrid "Teammates" feature. Sendgrid Teammates allows you to add and remove members of your team yourself without contacting the Content Catalyst helpdesk. Typical activities for members of your team might be to
- configure your account/domain to ensure your sender reputation is high to ensure email ends up in inboxes rather than in spam.
- check email activity
- see why that email wasn't received
🔔 If you aren't sure if you have a Sendgrid Teammates account please contact the Content Catalyst helpdesk.
Ensuring a high reputation
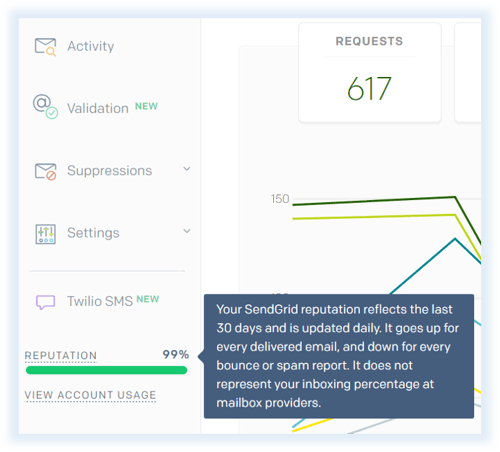
There are a number of ways to optimize emails sent from your site to ensure that they are successfully delivered to your users. You can view your reputation at the bottom of the Sendgrid navigation bar:
Our recommendations
- Configure your domain for email white labelling - now called domain authentication in Sendgrid
- Configure SPF for your domain
- Configure DKIM for your domain
- Consider configuring DMARC for your domain
- Configure your domain for email link white labelling - now called link branding in Sendgrid
- Work with your customers to ensure your domain is added to their mail server's white lists
1. Configure your domain for email white labelling - now called domain authentication in Sendgrid
Sendgrid have some excellent documentation on domain authentication:
How to set up domain authentication | SendGrid Documentation
Domain authentication (previously email whitelabelling) is the minimum that should be done and there is a detailed step by step in the above link.
2 & 3. Configure SPF & DKIM for your domain
When you compete domain authentication, Sendgrid handles some automatic SPF and DKIM records for you, which you can override if you want to set these up in a custom way.
SPF Records Explained | SendGrid Documentation
DKIM Records Explained | SendGrid Documentation
4. Consider configuring DMARC for your domain
Dmarc is an additional step:
Everything about DMARC | SendGrid Documentation
5. Configure your domain for email link white labelling - now called link branding in Sendgrid
Finally, you can apply link branding (previously called email link white labelling):
How to set up link branding | SendGrid Documentation
6. Work with your customers to ensure your domain is added to their mail server's white lists
The final item in the list will require you to engage with your customers by ensuring their technical teams do what they can to help your email get through. Unlike sending to private email addresses (Gmail, Yahoo, Hotmail etc.), businesses manage their own highly configured mail servers that have their own filtering rules. Whether it is part of your provisioning process for new customers or going back to existing ones, asking for your domains to be 'whitelisted' is probably the biggest factor in ensuring your emails get through.
What if we want to use our own Sendgrid account?
You can use and manage your own Sendgrid account. This would need to be paid for separately (a direct relationship between you and Sendgrid) the main benefit being the option to purchase a dedicated IP. Having a dedicated IP allows the configuration of rDNS which could enhance deliverability. To move to your own Sendgrid account you will first need to create this account directly with Sendgrid, then send us an API key with permission to send mail.
Finally, you need to supply to us the from address for emails sent from the platform, e.g. no-reply@yourdomain.com
Glossary
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): A domain record (DNS record) that says who can and can't send email for that domain - it is a tool used to help identify detect spam.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): An email authentication method developed by Yahoo! that checks an encrypted “key” embedded in each email sent against a list of public records to positively confirm the identity of the sender. In short, it helps ISPs identify the good mail and aids in preventing malicious email from getting through. It pretty much works the same way IP reputation does, except it works with your domain name.
- Dedicated IP: Instead of sharing an IP with others, a dedicated IP allows you more control of your email 'reputation' and, more importantly, improve deliverability by allowing the configuration of rDNS.
- rDNS: A mechanism that allows email servers that are receiving the email from you to determine what domain(s) you have associated with the IP address from which you are sending the email. The domain associated with the IP address may be checked (and potentially blocked) by the receiving mail server based on this check.
- Email white labelling: White labelling is the functionality that shows ISPs and recipient mail servers that the service sending the emails has your permission to do so on your behalf. There are several different components that you can white label: your sending domain, your dedicated IPs, and links to your websites and services.
- Email link white labelling: Email link white labels allow all of the click-tracked links to be from your domain instead of the mail handler's. It also will serve open tracking images from your domain. This helps in email deliverability because you are no longer relying on click tracking being routed through a domain that you do not control. Spam filters and recipient servers will look at the links within emails to determine whether the email should be delivered and will use the reputation of the root domain to determine whether the links can be trusted.
- Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance (DMARC): A further check that helps prevent phishing attacks by telling recipient mail servers what to do with mail that doesn't pass SPF and DKIM checks.
.png?width=200&height=89&name=CC%20logo%20blue-1%20(1).png)